Ethereum Layer 2’s Rise Towards Mass Adoption

The vision of a secure and user-friendly decentralized internet, supported by a shared economic framework and embraced by billions, relies on developing critical infrastructure. Scaling solutions, known as Layer 2, play a crucial role in constructing this foundation and enhancing Ethereum’s capabilities. These projects work together, forming a robust ecosystem that propels Ethereum towards its full potential.
In this article, we will delve into the innovations and narratives surrounding Layer 2 networks. We will discuss the challenges faced by these networks and their potential transformative impact on Ethereum’s mass adoption. Our analysis will be based on data from Footprint Analytics’ Layer 2 research page, providing valuable insights into this evolving ecosystem.
Why Do We Need Layer 2?
Blockchain technology has long been praised for its desirable qualities of decentralization, security, and scalability. However, the “blockchain trilemma” suggests that achieving all three simultaneously within a simple architecture is challenging. Ethereum, which currently processes over 1 million transactions per day, often faces high transaction fees due to increasing demand. To address this issue, Layer 2 networks have emerged as an innovative solution.
The primary objective of Layer 2 networks is to enhance transaction throughput by achieving higher transactions per second (TPS) while maintaining decentralization and security. These networks achieve this by consolidating multiple off-chain transactions into a single layer 1 transaction. As a result, transaction fees are significantly reduced, making Ethereum more accessible and inclusive for a wider range of users.
Different Types of Layer 2
Currently, there are three main types of Layer 2, including rollups, state channels and plasma.
Rollups
Rollups are layer 2 solutions that aggregate numerous transactions into a single transaction on layer 1, resulting in user cost savings by distributing transaction fees across participants within the rollup. There are two main types of rollups: optimistic rollups and zero-knowledge rollups (ZK-rollups). Optimistic rollups utilize fraud proofs to ensure the validity of off-chain transactions, while ZK-rollups employ zero-knowledge proofs to enhance privacy and security.
Examples of optimistic rollups include Arbitrum(Arbitrum One), Optimism(OP Mainnet), and Base.
Arbitrum, introduced by the Offchain Labs team in August 2021, has emerged as a prominent player in the industry, capturing a market share of over 50%. With its Nitro upgrade, Arbitrum has achieved full Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) equivalence, enabling developers to seamlessly migrate smart contracts from Ethereum to Layer 2 with minimal or no modifications required.
Optimism, the second-largest Ethereum Layer 2 solution, soft-launched its mainnet in January 2021 and became fully accessible to everyone in December 2021. Built with an EVM-equivalent architecture, Optimism offers a seamless scaling solution for Ethereum applications without encountering significant challenges.
Base, built on OP Stack in collaboration with Optimism, went live on the mainnet in July 2023. Within a few months, it achieved significant success, securing the third position in the Layer 2 market. Incubated by Coinbase, Base leverages Coinbase’s expertise in building crypto products.
On the other hand, ZK-rollup implementations include zkSync Era, Starknet, Linea, and Polygon zkEVM.
zkSync Era, recognized as the world’s first zkEVM blockchain, launched on the mainnet for all users in March 2023 and swiftly secured the fourth position in the Layer 2 market in terms of market share. zkSync Era has established itself as the dominant rollup solution in terms of user activities, including TPS and transactions.
Starknet went live on mainnet in November 2021. It achieves secure low-cost transactions and high performance by using the STARK cryptographic proof system. Starknet is powered by Cairo and as such is not EVM compatible. Efforts are underway to enable compatibility between Solidity and Cairo through the transpiler Warp.
Linea, a ConsenSys-powered Layer 2 solution, went live on the Ethereum mainnet in July 2023. It offers EVM compatibility, making it easy for developers to migrate and build applications on its network.
Polygon zkEVM public beta was launched in March 2023 and it provides EVM equivalence. Polygon, previously known as Matic, is a blockchain platform offering diverse blockchain solutions. Polygon zkEVM is one of the offerings from Polygon.
State channels
State channels are a mechanism that allows participants to conduct fast and unrestricted off-chain transactions, settling the final outcome on the Ethereum blockchain. This approach reduces network congestion, fees, and transaction delays.
The Raiden Network is an off-chain scaling solution that focuses on researching state channel technology, defining protocols, and developing reference implementations. It enables near-instant, low-fee, and scalable payments, making it compatible with any ERC20 token on Ethereum. The network aims to enhance scalability and usability while maintaining compatibility with the Ethereum ecosystem.
Plasma
A plasma chain is an independent blockchain that is connected to the main Ethereum chain through anchoring, and it utilizes fraud proofs, similar to optimistic rollups, to resolve disputes.
The OMG Network utilizes Layer-2 Plasma architecture, which offers robust safety assurances and high throughput. It provides a scalable solution for third-party developers interested in building decentralized payment applications on the Ethereum platform.
Data Insights
A consensus is forming: Ethereum will reach mass adoption, a matter of when, not if. So, how far is it?
Similar to the diffusion of other technologies, the adoption trajectory of Ethereum can be described by a classic bell curve. It begins with a limited number of innovators who are quick to embrace the technology, followed by the engagement of early adopters. As Ethereum continues to evolve and mature, it gradually expands its reach to encompass the early and late majority, leading to a mass adoption phase. Ultimately, the technology reaches the remaining segment of the population, referred to as the laggards, in its final phase of adoption.
Let’s explore the impact Layer 2 has on the mass adoption of Ethereum from these aspects:
TVL
Total value locked, or TVL, is anticipated to be the leading indicator of where adoption will occur.
As of October 2023, Arbitrum is leading the pack, with an impressive TVL of $6.00 billion and a market share of 61.03%, solidifying its position as the dominant player in the market. Optimism follows behind with a TVL of $2.60 billion and a market share of 26.41%, showcasing its substantial adoption and user engagement.
Other chains form the second echelon but their market shares fall far behind – less than 5%. Base, the newcomer, which was launched on the mainnet for everyone on July 13, 2023, secures the third spot with a TVL of $462.91 million. The zkSync Era network holds the fourth position with $450.87 million locked, while Starknet occupies the fifth place with a TVL of $135.27 million.
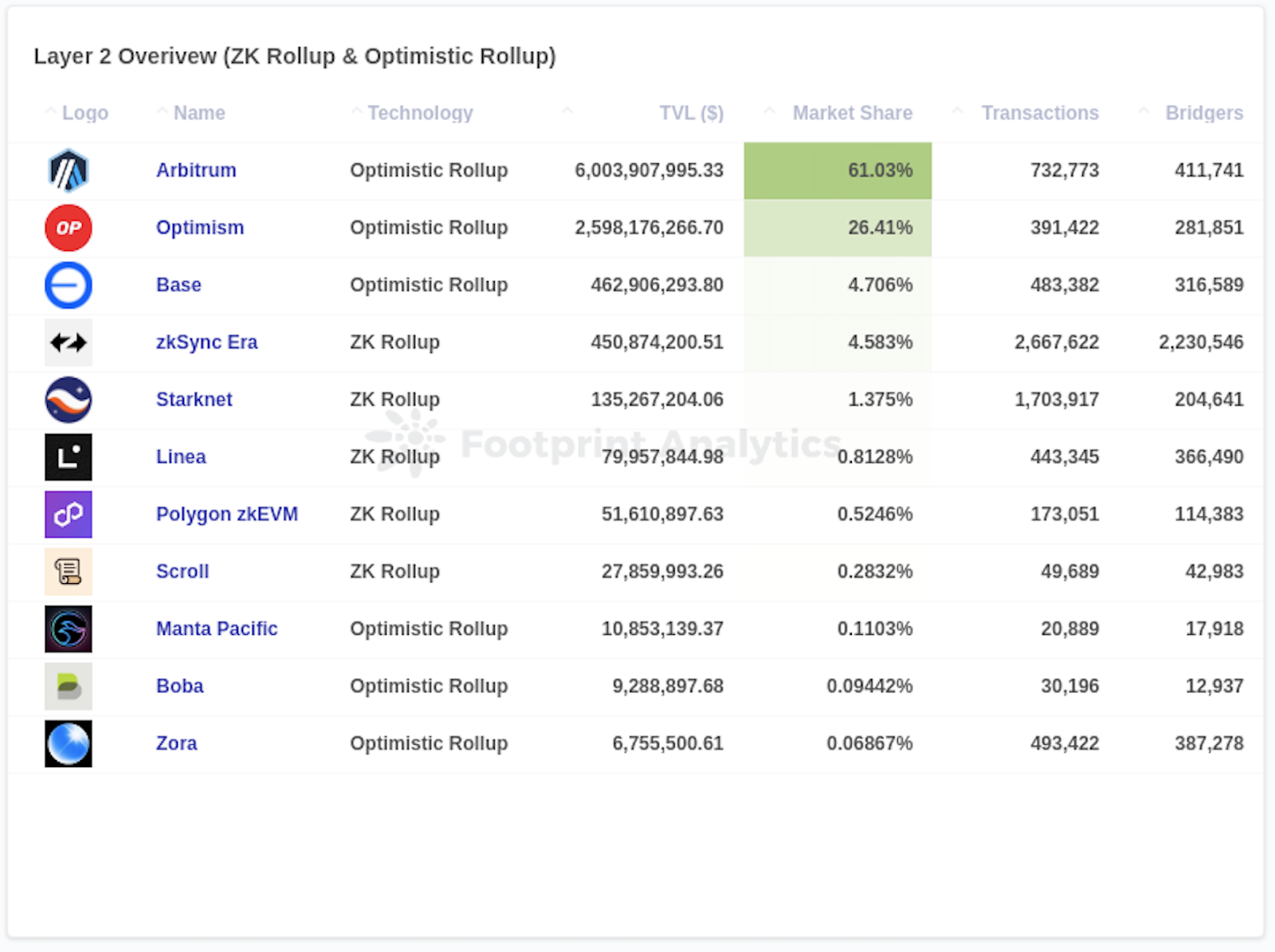
Source: Layer 2 Overview
Unique users and transactions
User activities, such as the number of unique users (referred to as “bridgers” who interact with Ethereum) and the volume of transactions, serve as key adoption indicators for adoption.
Among the various Layer 2 solutions, zkSync Era stands out as the frontrunner. It has accumulated an impressive 2.67 million unique users, accounting for 37.10% of all rollups, and facilitated 2.23 million transactions, representing 50.84% of rollup activity. zkSync Era’s initial airdrop activity attracted a significant number of users, and it has maintained its leading position since then. Starknet follows closely in terms of transaction volume, with 1.70 million transactions, constituting 23.70% of rollup activity.
Base and Linea, both launched on the mainnet in July 2023, have gained remarkable popularity in the market. They have surpassed Optimism and Polygon zkEVM in terms of both unique user engagement and transaction volume.
Throughput
One of the primary scaling challenges frequently discussed in the blockchain community pertains to transaction throughput.
At present, the Ethereum Mainnet has a capacity of approximately 15 transactions per second (TPS). In contrast, Visa boasts the ability to handle around 24,000 TPS, while Mastercard can process 5,000 TPS.
Layer 2 is bridging the gap for Ethereum. In October, the average TPS achieved by prominent rollups like Arbitrum and zkSync Era ranged from approximately 9.5 to 10, making them the closest in performance to the Ethereum network among the rollup solutions available. Rollups have collectively made significant contributions to scalability, surpassing the Ethereum mainnet by 321% in throughput, with a scalability factor of 4.21 in October.
While rollups contribute to scalability, no individual rollup currently surpasses Ethereum in terms of throughput. In a bear market, attracting and retaining users is challenging for both Layer 1 and Layer 2 networks. Building a prosperous Layer 2 ecosystem requires not only robust solutions but also high-traffic applications. Additionally, the user experience suffers due to the lack of seamless interaction between multiple Layer 2 solutions and between Layer 1 and Layer 2, for example, necessitating wallet switching and incurring liquidity costs.
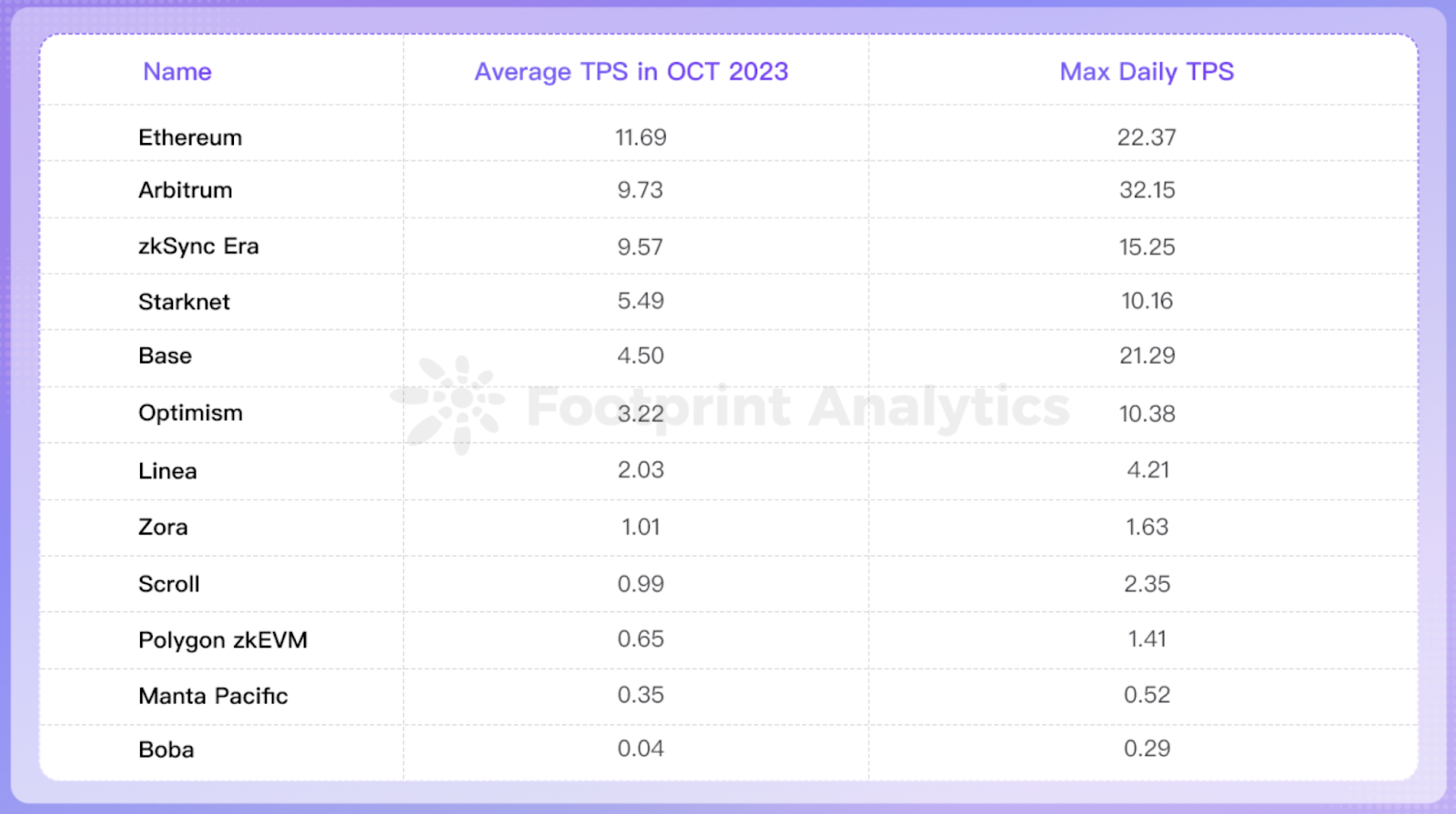
Cost
The adoption of layer 2 networks has played a crucial role in reducing network fees on Ethereum. By consolidating multiple off-chain transactions into a single layer 1 transaction, Ethereum has witnessed a significant decline in transaction fees.
According to Footprint Analytics, the average transaction fee in October 2023 for rollups was currently between 3% and 10% that of Ethereum.
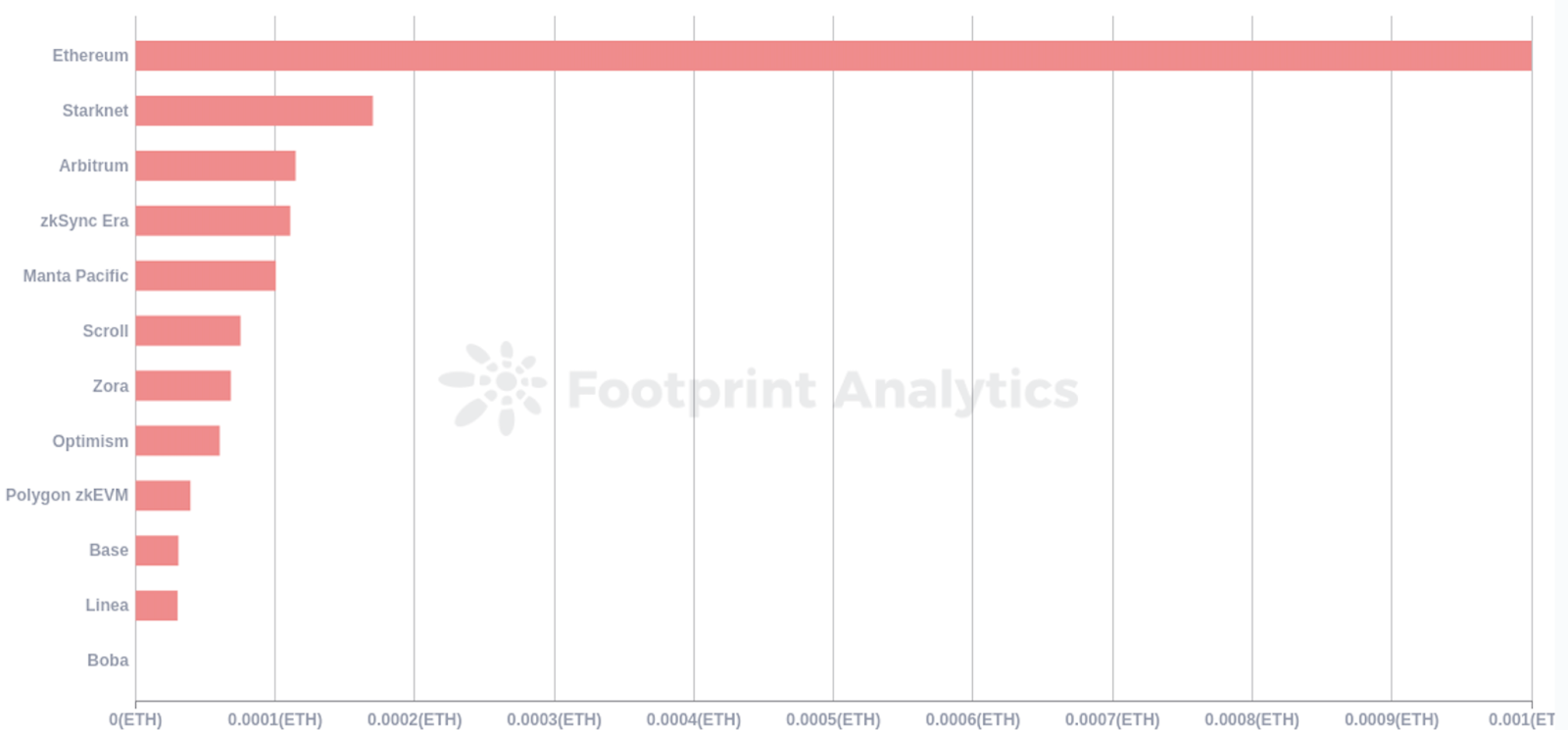
Source: Average Gas Fee
These figures underscore the increasing popularity and utilization of Layer 2 networks, highlighting their potential to alleviate congestion and enhance scalability on the Ethereum blockchain.
Innovations in Layer 2
In the dynamic landscape of blockchain technology, leading Layer 2 solutions such as Optimism, zkSync, and Arbitrum are actively pursuing innovative approaches to address persistent challenges while maintaining a focus on interoperability. These prominent players maintain a rapid pace of innovation, including technology and application, continually striving to stay ahead and retain their competitive edge in the market.
The Superchain, proposed within the Optimism ecosystem, is a network of rollup networks that share a common codebase called the OP Stack. This framework aims to establish an interoperable environment where various layer 2 networks can communicate and transact with each other, similar to how the internet enables communication between devices. By providing horizontal scalability, the Superchain addresses challenges associated with traditional multi-chain architectures. These challenges include differentiated security architectures among parallel chains, which can lead to increased systemic risk as more chains are added, and the cost of setting up new nodes for each additional chain.
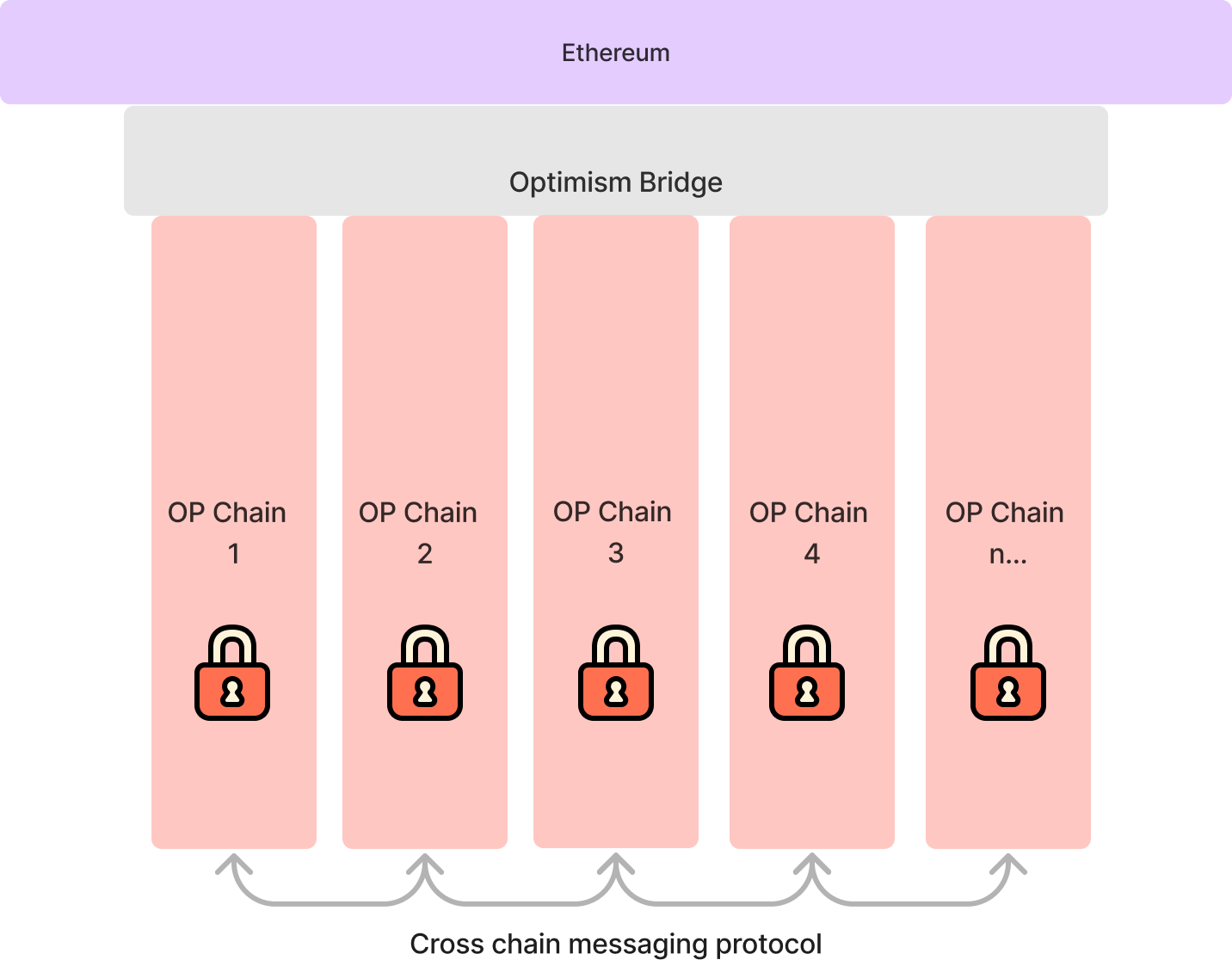
Source: Superchain – OP Stack Docs
In June 2023, zkSync introduced “Hyperchains“, a novel network that operates as fractal-like instances of zkEVM. These Hyperchains run in parallel with a shared settlement on Layer 1, offering the flexibility of functioning as Layer 2 networks alongside zkSync Era or as Layer 3 Validiums. Hyperchains within the zkSync ecosystem can be developed and deployed by anyone without the need for permission. To ensure trust and seamless interoperability, each Hyperchain must be powered by the same zkEVM engine available on the ZK Stack. GRVT, a hybrid crypto exchange combining centralized and decentralized exchange benefits, will be the first hyperchain in the zkSync ecosystem. Its closed alpha version is expected to launch in November 2023, followed by the mainnet release in Q1 2024.
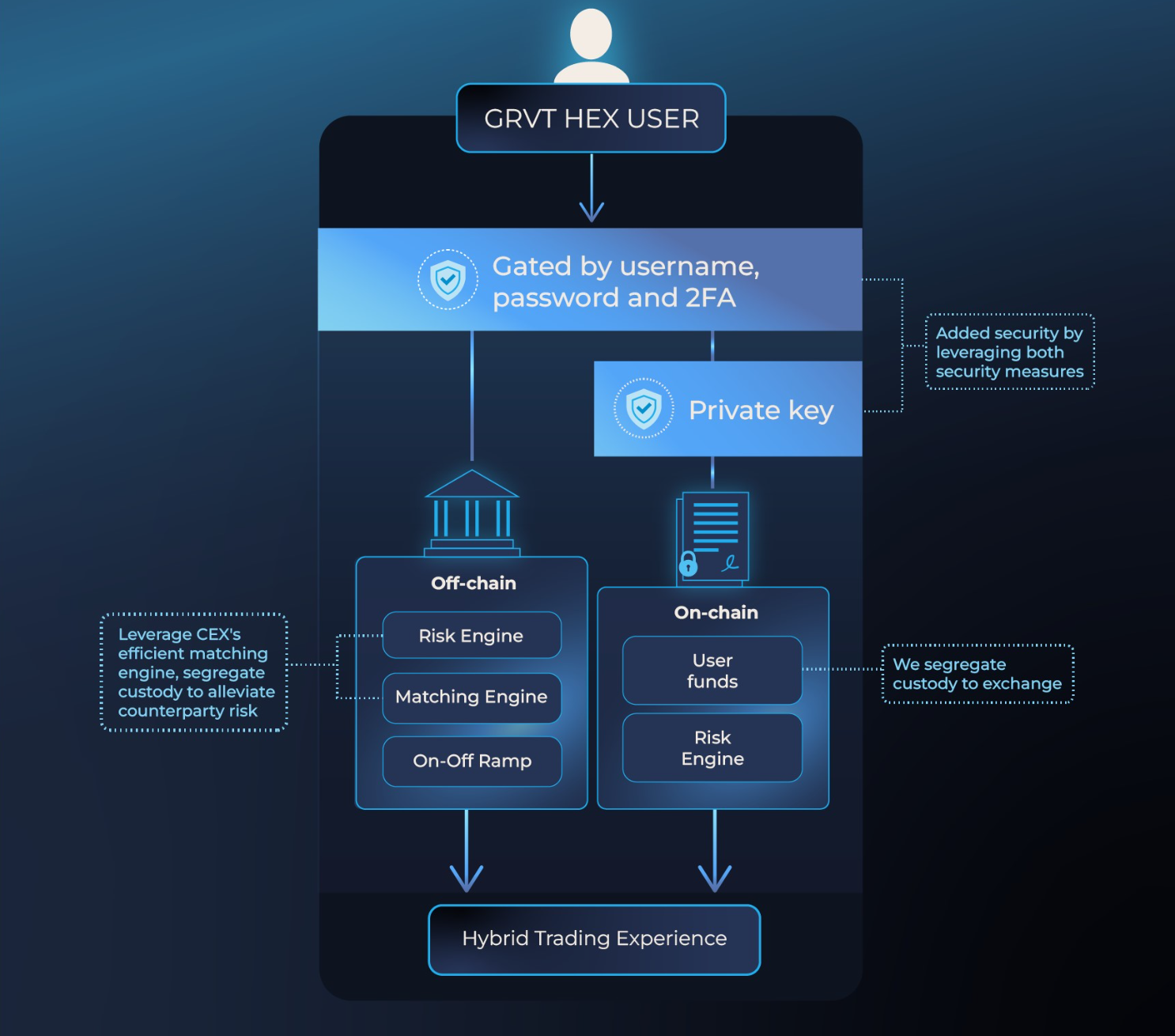
Source: Architecture – GRVT
Arbitrum Stylus, launched by Arbitrum in August 2023, allows smart contract development in multiple programming languages such as Rust, C, and C++ on their Layer 2 network. In addition to Solidity, developers can now write smart contracts in languages compatible with WebAssembly (WASM). WASM enables running code from languages like Rust and C++ on the web, and with Arbitrum Stylus, on the blockchain as well. Stylus introduces a second, co-equal virtual machine that is fully interoperable with the EVM, offering a new approach to writing smart contracts.
Narratives in Layer 2
Layer 2 itself has emerged as a prominent narrative in the cryptocurrency space since 2022. Within the realm of Layer 2, narratives have played a significant role in shaping public perception and subsequently influencing market movements. These narratives provide insights into the future of Layer 2 and Ethereum as a whole.
- Fully on-chain games. These games utilize the blockchain as an alternative to centralized game servers, incorporating every aspect of the game on-chain, including assets, logic, state, and storage. Starknet and COMBO(live on testnet currently) have positioned themselves as a prominent supporter of fully on-chain games within the realm of public chains.
- Modular blockchains. Initially, blockchains were designed with a monolithic approach, where a single blockchain handled all tasks. However, the concept of modular blockchains emerged to specialize in specific functions rather than attempting to cover everything. Celestia is the first modular blockchain network. It’s ready to launch and unveiled the airdrop and launch plans in October 2023.

- Zero gas fee. Gas fees have been a significant hurdle for the mass adoption of Ethereum. To address this pain point, GasZero(live on testnet currently) has emerged as a Layer 2 blockchain network that offers a unique solution: it charges zero gas fees for trusted end users. On GasZero, users can interact with decentralized networks and smart contracts without the need for any tokens in advance in their wallets.
- Layer 3. The concept of “Layer 3” in the blockchain industry does not have a widely accepted definition at the moment. Vitalik Buterin, co-founder of Ethereum, believes that it is premature to establish definitive definitions because the architecture of the multi-rollup ecosystem is still evolving, and most discussions are theoretical in nature. However, Buterin has shared three visions of what Layer 3s could potentially represent in the future.
- Layer 2 is for scaling, and Layer 3 is for customized functionality, for example, privacy.
- Layer 2 is for general-purpose scaling, and Layer 3 is for customized scaling.
- Layer 2 is for trustless scaling (rollups), and Layer 3 is for weakly trusted scaling (validiums).
Challenges Faced by Layer 2
The growing popularity of cost-effective and efficient Layer 2 networks as alternatives to the congested Ethereum network has gained considerable attention. It is crucial to maintain a robust base layer while cautiously expanding certain aspects of its capabilities. Within the Ethereum community, the evolution of technology and applications is encouraged, but maintaining a delicate balance between user-friendliness and the benefits of decentralization is of utmost importance, as emphasized by Vitalik Buterin during the Ethereum Hong Kong Hackathon in October 2023.
Layer 2 networks face four critical challenges in their quest for scalability on Ethereum according to Buterin.
- Proof system security and decentralization. Validity (ZK) proofs and fraud proofs are employed to demonstrate the legitimacy of transactions without requiring processing on the main Ethereum chain. However, validity proofs face centralization concerns due to their reliance on specific hardware.
- Sequencing decentralization. These sequencers verify, order, and compress transactions for transfer to Layer 1. However, this centralized setup has drawn criticism for its potential as a single point of failure, censorship vulnerability, or susceptibility to shutdown by authorities.
- Cross-L2 wallets. They enable seamless interaction with multiple Layer 2 solutions without the need for wallet switching.
- Data availability. It refers to on-chain data availability, the challenge of storing a full copy of the blockchain data to validate transactions. It is worth noting that solutions like Validiums and Optimiums are not typically categorized as Layer 2s because they do not publish data on Layer 1. Instead, they introduce additional trust assumptions on top of Layer 1.
In addition, as we mentioned earlier, no individual Layer 2 currently surpasses Ethereum in terms of throughput. It’s urgent to develop the ecosystem within each network.
- Ecosystem and dApps. Currently, Layer 2 networks host various protocols in their ecosystems, with the majority of them being in the DeFi space. By bringing in phenomenal dApps, Layer 2 networks can expand their ecosystem and attract more users, encouraging them to stay.
Ending Words
In conclusion, Layer 2 networks are propelling Ethereum one step closer to mass adoption by effectively tackling the scalability and cost challenges that have hindered its progress. These networks offer innovative solutions that enhance transaction throughput and reduce fees, making Ethereum more accessible and inclusive for a wider audience.
Furthermore, beyond Ethereum’s Layer 2 networks, opBNB has emerged as BNB Chain’s response to the scalability challenge. In September 2023, opBNB successfully completed the public launch of its mainnet. Indeed, the responses and future directions of other public chains in the face of these challenges are equally tantalizing. The key emphasis remains on ecosystem development and user attraction. The vast expanse of possibilities stretches out before us, as each chain embarks on its own unique path towards scalability and mass adoption.