What Is Bitcoin Halving? An Overview and History of BTC Halvings

Hundreds of new cryptocurrencies join the market every year, but Bitcoin still stands above them all. Its success can be attributed to many factors, like its mainstream recognition, pioneering status and, of course, its meticulously designed economic principles.
Central to this design is Bitcoin mining — a process that allows miners to receive rewards for validating transactions. However, unlike many assets, Bitcoin has a limited supply. As a result, periodically, the mining reward is halved in an event known as “halving.” I’ve seen firsthand how these halvings can create waves in the crypto industry, influencing both Bitcoin’s price and the general market sentiment. In this article, I’ll take a look at what Bitcoin halvings are, why they take place, and how they can impact the rest of the crypto industry.
What Is Bitcoin Halving?
Bitcoin, one of the world’s most well-known digital currencies, has a unique monetary policy built into its code. At its heart is an event known as the Bitcoin halving. This event is essentially a reduction in the block rewards received by miners for verifying and adding transactions to the blockchain.
Initially, when Bitcoin was created, miners received 50 BTC per block as their reward. However, every 210,000 blocks, or approximately every four years, this reward is cut in half. So, after the first halving, it dropped to 25 Bitcoins per block, to 12.5 after the next, and so on.
What Happens During a Bitcoin Halving?
During a BTC halving:
- Block rewards that miners receive for adding new transactions to the blockchain are reduced by 50%.
- As a result, the BTC per block that miners receive as their reward for mining decreases, making the overall inflation rate of Bitcoin drop.
- Transaction fees do not get halved. They continue to provide an incentive for miners to keep the network secure, especially as block rewards decrease over time.
- The crypto market often reacts to this event with increased speculation and discussions about Bitcoin’s future value and role in the financial ecosystem.
Why Do Bitcoin Halvings Occur?
Bitcoin halvings are integral to its design and have several purposes:
- Controlled Supply. Unlike fiat currencies that can be printed in unlimited quantities by central banks, Bitcoin has a maximum supply of 21 million coins. The halving mechanism ensures that these Bitcoins are introduced into the system gradually, which makes it a deflationary asset over time.
- Reduced Inflation. By decreasing the rewards for miners, the inflation rate of Bitcoin is lowered. This is in stark contrast to traditional fiat currencies, where inflation can be influenced by external factors such as political decisions or economic conditions.
- Sustainability. The halving process ensures that all 21 million Bitcoins won’t be mined too quickly, giving the Bitcoin network more time to grow, mature, and become widely adopted.
- Miner Incentive. Although block rewards decrease, the hope is that the increasing value of Bitcoin, coupled with transaction fees, will continue to provide a lucrative incentive for miners to maintain the network’s security and integrity.
Essentially, while Bitcoin and other digital assets continue to evolve in the ever-changing crypto market, the halving mechanism serves as a balancing act, regulating Bitcoin’s supply and, by extension, its value against traditional assets and currencies. It stands as a testament to Bitcoin’s promise to challenge the status quo of central banks and traditional fiat currencies, offering an alternative in the form of decentralized digital currency.
Bitcoin Halving History
The Bitcoin halving event plays a pivotal role in shaping Bitcoin’s economic model and market dynamics. Over the years, there have been several such events, each influencing Bitcoin miners, Bitcoin transactions, and the overall crypto market in their own unique ways. Diving into the Bitcoin halving dates history can give us a broader understanding of its impact on the digital currency’s landscape.
First Bitcoin Halving (2012)
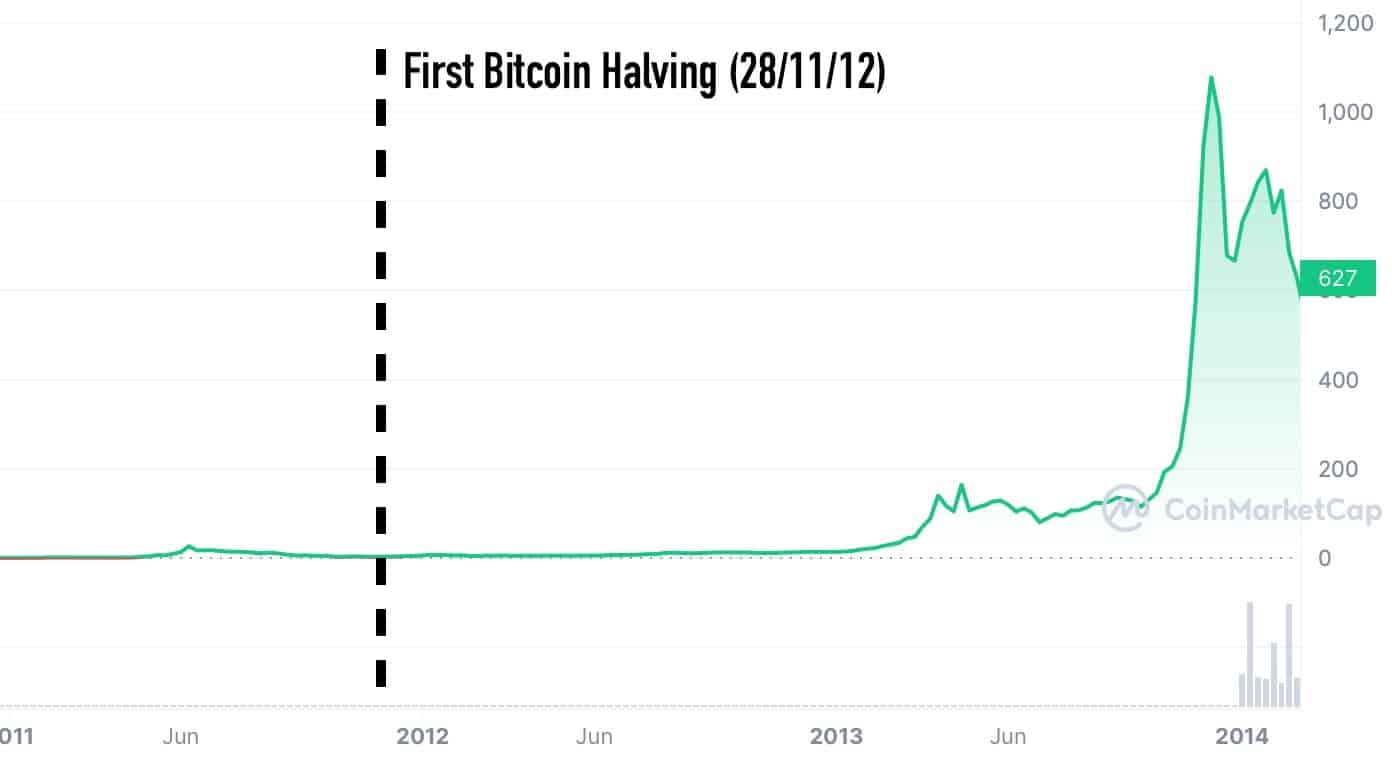
Date: November 28, 2012
Block Reward Before Halving: 50 BTC
Block Reward After Halving: 25 BTC
The first Bitcoin halving was a significant milestone, coming just three years after Bitcoin’s launch. This event set the precedent for future halvings. While it was a moment of intrigue within the crypto community, the wider world was still acquainting itself with the concept of Bitcoin. In the aftermath of this halving, Bitcoin’s price experienced a steady ascent, signaling the potential for future price surges.
Second Bitcoin Halving (2016)
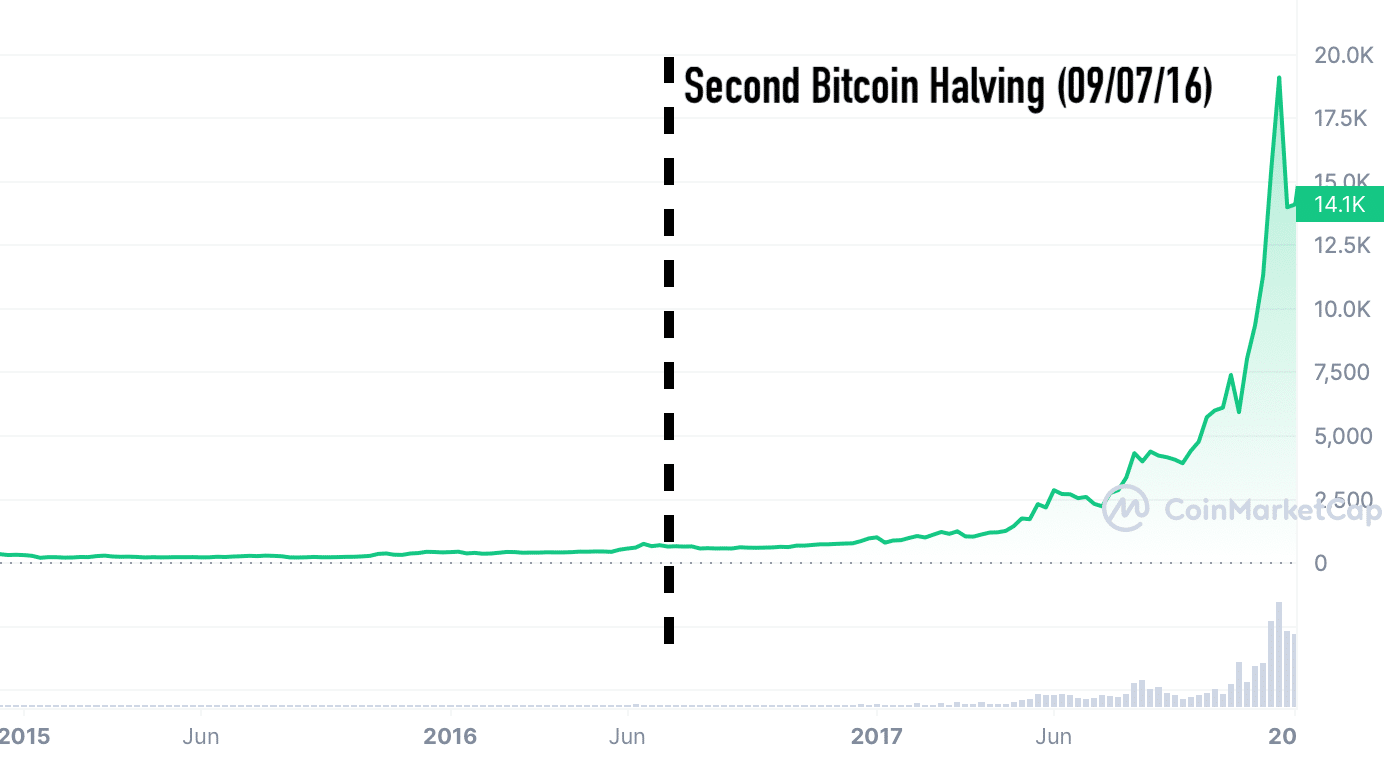
Date: July 9, 2016
Block Reward Before Halving: 25 BTC
Block Reward After Halving: 12.5 BTC
By the second halving event, Bitcoin had garnered significant attention. The crypto market watched eagerly, and the event did not disappoint. In the ensuing months, Bitcoin’s value started climbing, culminating in the remarkable bull run of 2017.
Third Bitcoin Halving (2020)
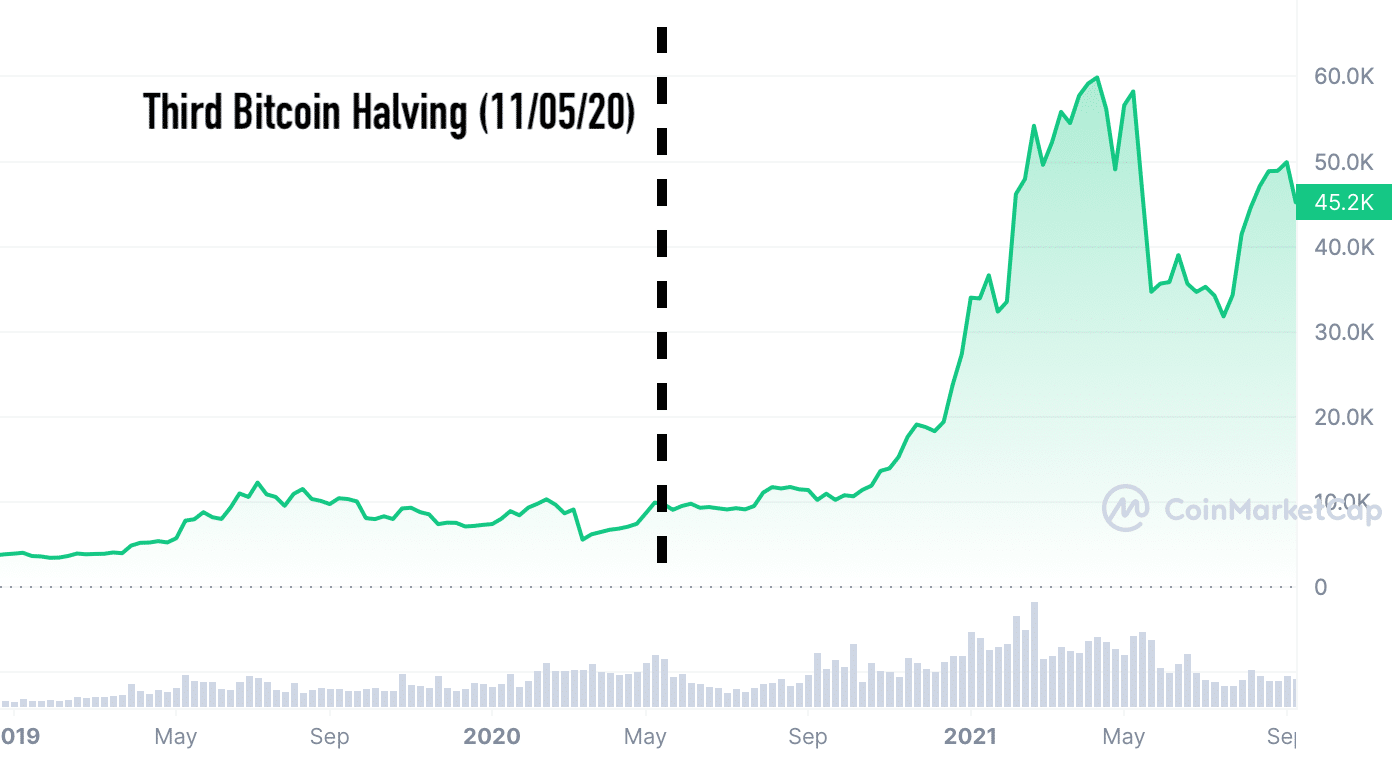
Date: May 11, 2020
Block Reward Before Halving: 12.5 BTC
Block Reward After Halving: 6.25 BTC
The third Bitcoin halving event was met with much anticipation. With a growing acknowledgment of digital currencies and their potential to reshape financial systems, this halving drew immense attention. Following this event, despite several global economic challenges, Bitcoin’s resilience shone through as it ventured into new all-time price highs.
When Is the Next Bitcoin Halving?
The Bitcoin protocol specifies that a halving event occurs every 210,000 blocks. Given that the last halving took place in May 2020 at a block height of 630,000, the next halving is anticipated around the 840,000th block. If we consider that a new block is added to the Bitcoin blockchain approximately every 10 minutes, the next halving is projected to occur in 2024.
FAQ
How does Bitcoin halving work?
Every 210,000 blocks, the block reward given to Bitcoin miners for processing Bitcoin transactions and adding them to the Bitcoin blockchain is reduced by 50%. This event is hardcoded into the Bitcoin protocol, ensuring that the total Bitcoin supply doesn’t exceed its cap of 21 million.
What happens when there are no more Bitcoins left?
Bitcoin has a capped supply of 21 million coins. As of now, the majority of these coins have already been mined, but it will take until approximately the year 2140 for the last Bitcoin to be mined. After the last BTC has been mined, miners will no longer receive block rewards in the form of new Bitcoins.
Instead, their incentive to keep validating transactions and maintaining the network’s security will come solely from transaction fees. The Bitcoin protocol has been designed with this eventual scenario in mind, emphasizing the importance of transaction fees in the long-term sustainability of the Bitcoin blockchain.
Will Bitcoin price rise after the next halving?
While past events provide insights, they don’t necessarily dictate future outcomes. Yet, they undoubtedly underscore the significance of the halving mechanism in Bitcoin’s design. Historically, previous halvings have been followed by periods of significant price appreciation for Bitcoin. However, it’s essential to understand that numerous factors influence the price of Bitcoin, including but not limited to market demand, global economic conditions, regulatory developments, and technological advancements.
While the reduction in the mining reward tends to lessen the selling pressure from miners (since they have fewer Bitcoins to sell), there’s no guaranteed outcome. Past price movements post-halving serve as a reference, but they don’t predict future performance. It can be beneficial to study trends following previous halvings for informational purposes, but one should approach the future with an understanding of Bitcoin’s broader ecosystem and the myriad of factors that can influence its value.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.