Which Model Describes How Data is Written to a Blockchain

Blockchain
- Introduction
- Which Model Describes How Data is Written to a Blockchain
- Blockchain Architecture and Data Storage Methods
- Blockchain Architecture and Data Writing
- Transaction Validation and Consensus Mechanisms
- Block Creation and Digital Signatures
- Merkle Trees and Data Organization
- Block Confirmation and Chain Integrity
- Smart Contracts and Programmable Transactions
- Blockchain Architecture and Data Storage Methods
- Ledger Synchronization and Transaction Processing
- Immutable and Unalterable Records
- Time-Stamping Methods and Block Verification
- Data Security and Protection
- Conclusion
- FAQ
Introduction
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing various industries by offering a new way to store and manage data through its unique distributed ledger system. As a decentralized network, it maintains data integrity and security, ensuring transparency and trust among its users. This article aims to shed light on the specific model that describes how data is written to a blockchain, covering essential aspects such as cryptography, consensus algorithms, and the role of digital signatures, as well as the importance of immutable records and data security. So which model describes how data is written to a blockchain?
Which Model Describes How Data is Written to a Blockchain
Blockchain Architecture and Data Writing/Storage Methods
The blockchain architecture consists of a distributed ledger system that stores data in a series of interconnected blocks. Each block contains a set of transactions or data entries, which are securely written and stored in the network using advanced cryptographic techniques and hash algorithms. The process of writing data to a blockchain involves several steps, including transaction validation, block formation, and block verification.
Transaction Validation and Consensus Mechanisms
Before writing data to the blockchain, transactions need to be validated to ensure their authenticity and prevent double-spending. This is achieved through various consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), which require participants to solve complex mathematical problems or prove ownership of a certain amount of cryptocurrency.
These consensus algorithms maintain the decentralized nature of the blockchain and promote fairness among participants. They also help to synchronize the ledger across the peer-to-peer (P2P) network, ensuring that every node has a consistent copy of the distributed ledger.
Block Creation and Digital Signatures
Once transactions are validated, they are grouped into a block, along with a unique identifier known as a hash. The hash is generated using hash functions, which take the input data and produce a fixed-size output. Digital signatures, a form of digital authentication, are also used to verify the identity of the sender and ensure the transaction’s integrity.
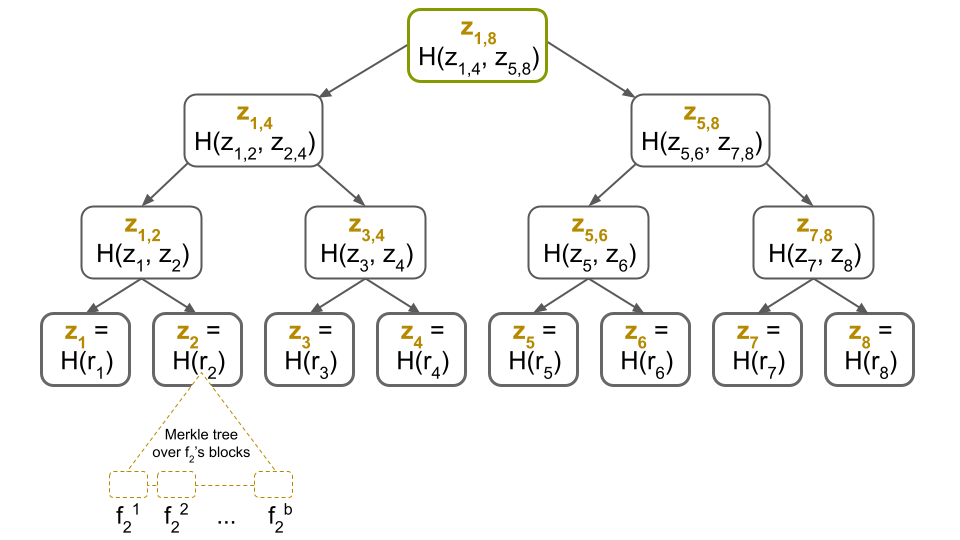
Merkle Trees and Data Organization
The data within a block is organized using Merkle trees, a data structure that simplifies the verification process by allowing nodes to check the validity of a transaction without requiring the entire block’s information. Each Merkle tree consists of a root hash, which represents the combined hash of all the transactions in the block.
Block Confirmation and Chain Integrity
Once a block is created, it must be confirmed and added to the existing blockchain. This process involves a timestamping method that records the block’s creation time and ensures the immutability of the records. Additionally, the newly created block’s hash is linked to the previous block’s hash, establishing a chain of interconnected blocks.
This chain integrity ensures that any attempt to alter a transaction would require changing all the subsequent blocks in the chain, which is practically impossible due to the immense computational power needed to recalculate the hashes.
Smart Contracts and Programmable Transactions
Blockchain technology also supports smart contracts, which are programmable transactions that automatically execute when predetermined conditions are met. These self-executing agreements enable a wide range of applications, from asset management to supply chain tracking.

Blockchain Architecture and Data Storage Methods
The blockchain architecture consists of a distributed ledger system that stores data in a series of interconnected blocks. Each block contains a set of transactions or data entries, which are securely written and stored in the network using advanced cryptographic techniques and hash algorithms. The process of writing data to a blockchain involves several steps, including transaction validation, block formation, and block verification.
Ledger Synchronization and Transaction Processing
Before writing data to the blockchain, transactions need to be validated and processed to ensure their authenticity and prevent double-spending. This is achieved through various consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), which require participants to solve complex mathematical problems (mining process) or prove ownership of a certain amount of cryptocurrency (staking systems).
These consensus algorithms maintain the decentralized nature of the blockchain and promote fairness among participants. They also help to synchronize the ledger across the peer-to-peer (P2P) network, ensuring that every node has a consistent copy of the distributed ledger, which is essential for chain consistency and P2P communication.
Immutable and Unalterable Records
One of the main advantages of blockchain technology is the creation of immutable and unalterable records. Once data is written to a block and confirmed, it becomes virtually impossible to modify or delete it without altering the entire chain. This feature ensures data security and protection against malicious activities, providing a high level of trust among users.
Time-Stamping Methods and Block Verification
Once a block is formed, it must be verified and added to the existing blockchain. This process involves time-stamping methods that record the block’s creation time and ensures the immutability of the records. Additionally, the newly created block’s hash is linked to the previous block’s hash, establishing a chain of interconnected blocks that ensures chain consistency.
Data Security and Protection
Blockchain technology offers a high level of data security and protection through the use of cryptographic techniques, digital signatures, and distributed systems. These features, combined with the inherent immutability of records, make the blockchain a robust solution for data storage and management.
Conclusion
In summary, the model that describes how data is written to a blockchain involves several key components, including transaction validation, consensus mechanisms, block formation, and chain integrity. The use of cryptographic techniques, digital signatures, and distributed systems ensures the security and immutability of data stored in a blockchain. As the technology continues to evolve, it is expected to play an increasingly significant role in various industries, transforming the way we store, manage, and share data while maintaining the highest standards of data security and protection. After reading this article, it should be clear which model describes how data is written to a blockchain. More information in the FAQ below.
FAQ
What is the main purpose of blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology aims to provide a new way of storing and managing data through a unique distributed ledger system. It maintains data integrity and security while ensuring transparency and trust among its users.
What are the key components of the blockchain architecture?
The blockchain architecture consists of a distributed ledger system that stores data in a series of interconnected blocks. Each block contains a set of transactions or data entries, which are securely written and stored using cryptographic techniques and hash algorithms.
How are transactions validated in a blockchain?
Transactions are validated using various consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). These mechanisms require participants to solve complex mathematical problems or prove ownership of a certain amount of cryptocurrency to maintain the decentralized nature of the blockchain and promote fairness.
What is the role of digital signatures in blockchain technology?
Digital signatures serve as a form of digital authentication, verifying the identity of the sender and ensuring the integrity of a transaction.
How does blockchain technology ensure data security and protection?
Blockchain technology offers data security and protection through the use of cryptographic techniques, digital signatures, and distributed systems. These features, combined with the inherent immutability of records, make the blockchain a robust solution for data storage and management.
What are smart contracts, and how are they used in blockchain applications?
Smart contracts are programmable transactions that automatically execute when predetermined conditions are met. These self-executing agreements enable a wide range of applications, from asset management to supply chain tracking.
What are the main advantages of using blockchain technology for data storage?
Blockchain technology offers several advantages for data storage, including the creation of immutable and unalterable records, high data security and protection, and the ability to synchronize the ledger across a decentralized peer-to-peer (P2P) network for chain consistency and communication.
How does blockchain technology maintain chain consistency?
Blockchain technology maintains chain consistency by ensuring that every node in the peer-to-peer (P2P) network has a consistent copy of the distributed ledger. This is achieved through consensus algorithms, which help synchronize the ledger and promote fairness among participants.
READ MORE:
How Can Features of Blockchain Support Sustainability Efforts
How Does Blockchain Technology Help Organizations When Sharing Data?
Which Statement is True About Blockchain?
How Does Blockchain Support Data Privacy?
How is Blockchain Different from Traditional Database Models?